Firmware camera controller based on ESP32
Contact UsAbout This
This article describes the implementation of a network bridge using the ESP32 to enable Ethernet-based IP cameras to transmit Real Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) video streams over a Wi-Fi connection. The solution configures the ESP32 as a Wi-Fi Access Point (AP), allowing connected client devices to receive and display video streaming from the Ethernet-connected IP camera to the ESP32 board. As a result, any device with Wi-Fi connectivity, such as a smartphone, PC or tablet, can connect to the Wi-Fi network created by the ESP32-based board and view the real time video stream from the IP camera. This represents a functional and adaptable solution to extend connectivity and simplify the integration of video systems in different application scenarios.
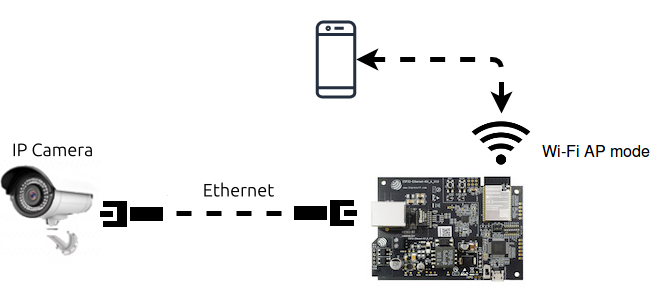
The architecture
The architecture of the solution involves using the ESP32 to manage data traffic between its Ethernet interface and its Wi-Fi interface. The operating process is as follows:
IP Camera Connection: A standard IP camera (camera module) with Ethernet port is physically connected to the Ethernet port of the ESP32 board.
Ethernet Data Reception: The ESP32 receives network packets, containing the RTSP stream, sent by the IP camera via the Ethernet connection.
Wi-Fi Access Point Configuration: The ESP32 is configured to operate as a Wi-Fi access point, creating a wireless network to which client devices can connect.
Data Forwarding via Wi-Fi: RTSP packets received via Ethernet are forwarded by the ESP32 via its Wi-Fi interface to clients connected to its network.
RTSP Streaming Viewing: Client devices connected to the ESP32’s Wi-Fi network can establish an RTSP connection with the IP camera (via the IP of the camera and the RTSP port) and view the video stream.
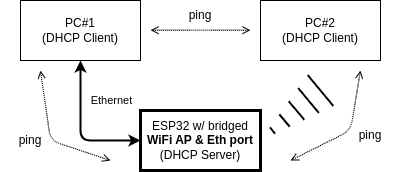
Key advantages
Implementing this Ethernet-Wi-Fi bridge with ESP32 offers the following practical benefits:
Extended connectivity: Allows the use of IP cameras (camera module) with only Ethernet interface in environments with Wi-Fi connectivity, maintaining a responsive and real-time video streaming.
Installation flexibility: Simplifies the positioning of cameras in scenarios where Ethernet cabling is not convenient, without compromising real-time video viewing.
Wireless access to real-time stream: Allows Wi-Fi connected devices to access and view the real-time video streaming of the IP camera.
Versatility: The operating principle can be extended and adapted to different applications that require wireless transmission of data from Ethernet devices, including video surveillance systems with various types of IP cameras, ensuring real-time video viewing.
More functionalities: Allow the iot device to perform operation based on client connect to him using wifi
Integration into Larger IoT Systems
In addition to its specific application as an IP camera bridge, the versatility of the ESP32 opens up interesting prospects for the integration of this solution into much larger IoT projects. With its multiple features, including Wi-Fi, MQTT and Bluetooth connectivity, processing capabilities and various interfaces, the ESP32 represents a key element for the realization of complete and integrated solutions. The ability to connect Ethernet devices to Wi-Fi networks and manage real-time data flows, such as RTSP video streaming, makes this bridge a valuable component in complex IoT architectures that require the wireless collection and transmission of video data from wired devices. Our current implementation of this IP camera bridge is a concrete example of how we leveraged the potential of the ESP32 to provide innovative solutions. We are already implementing integrations of this principle into larger IoT projects, where the ESP32’s ability to interact with other devices and platforms, combined with its reliability and low cost, offers significant added value for the creation of embedded, complete and innovative products.